Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 and Cs
and Cs ions in compacted bentonite, 2
ions in compacted bentonite, 2Sato, Haruo
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.932, p.905 - 912, 2006/00
Non-steady state diffusion experiments for I and Cs
and Cs ions in compacted Na-smectite were performed in the parallel and perpendicular directions to the orientated direction of smectite particles as a function of smectite's dry density (0.9-1.4 Mg/m
ions in compacted Na-smectite were performed in the parallel and perpendicular directions to the orientated direction of smectite particles as a function of smectite's dry density (0.9-1.4 Mg/m ), salinity ([NaCl]=0.01, 0.51 M) and temperature (295-333 K), and the anisotropies and the effect of salinity in the apparent diffusivities (Da) and activation enthalpies (Ea) for both ions were discussed. The Na-smectite was prepared by ion-exchanging with Na
), salinity ([NaCl]=0.01, 0.51 M) and temperature (295-333 K), and the anisotropies and the effect of salinity in the apparent diffusivities (Da) and activation enthalpies (Ea) for both ions were discussed. The Na-smectite was prepared by ion-exchanging with Na ions a Na-bentonite, Kunipia-F, of which smectite content is over 99 wt.%. The Da-values for both ions tended to be higher in the parallel direction than in the perpendicular direction to the orientated direction of smectite particles. The Da-values of I
ions a Na-bentonite, Kunipia-F, of which smectite content is over 99 wt.%. The Da-values for both ions tended to be higher in the parallel direction than in the perpendicular direction to the orientated direction of smectite particles. The Da-values of I ions in the parallel direction decreased with increasing salinity only at low-dry density, but those of Cs
ions in the parallel direction decreased with increasing salinity only at low-dry density, but those of Cs ions elevated with increasing salinity for all conditions. Based on this, it is interpreted that I
ions elevated with increasing salinity for all conditions. Based on this, it is interpreted that I ions mainly diffuse in interstitial pores and Cs
ions mainly diffuse in interstitial pores and Cs ions diffuse in both interlayer and interstitial pores. The Ea-values for I
ions diffuse in both interlayer and interstitial pores. The Ea-values for I ions, similar levels to that for the ionic diffusivity in free water (Do) of I
ions, similar levels to that for the ionic diffusivity in free water (Do) of I ions at low-dry density, elevated with increasing dry density. The Ea-values for Cs
ions at low-dry density, elevated with increasing dry density. The Ea-values for Cs ions, higher than that for the Do of Cs
ions, higher than that for the Do of Cs ions even at low-dry density, elevated with increasing dry density. Such high Ea-values for Cs
ions even at low-dry density, elevated with increasing dry density. Such high Ea-values for Cs ions are considered to be due to the effects of the ion exchange enthalpy between Cs
ions are considered to be due to the effects of the ion exchange enthalpy between Cs and Na
and Na ions in smectite and the decrease in the activity of porewater.
ions in smectite and the decrease in the activity of porewater.
Nakayama, Masashi; Iriya, Keishiro*; Fujishima, Atsushi; Mihara, Morihiro; Hatanaka, Koichiro; Kurihara, Yuji*; Yui, Mikazu
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.932, p.159 - 166, 2006/00
Cementitious material is one of candidates of engineered barriers in TRU and HLW repositories. However, since ordinary Portland cement may rises pH of pore water due to its high alkalinity, bentnite and rock which contact with cementitious barriers as a mulch barrier system may deteriorate for a long term by its high pH. Low alkalinity cement with high pozzolanic material content are developed in order to reduce such hyper alkaline deterioration. This paper shows that pH of pore water of this cement is about 11, and that it can be applied for actual structures as self compacting concrete and shotcrete.
Tanai, Kenji; Yui, Mikazu
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.932, p.127 - 134, 2006/00
None
Nishimura, Mayuka; Hirai, Takashi*; Tanai, Kenji; Yui, Mikazu
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.932, p.227 - 234, 2006/00
The objective of this study is to clarify mechanical effect of engineered barrier system to a fault movement presupposed to occur on geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The plan of this study is; (1) to understand mechanical behavior of buffer when shearing takes place in laboratory simulated tests, and (2) to make progress in numerical analysis techniques in order to estimate the effect of fault movement on engineered barrier system on disposal site. Accordingly, first, laboratory simulated tests were carried out with a 1:20 model of engineered barrier system. The experimental results represented that the increased total pressure was mainly due to the increase of pore water pressure. Secondly, the model test was simulated with the help of the finite element method. The calculation results showed that the degree of water draining from buffer into outside affected on the behavior of the pressure increase. It also showed the calculation expressed the experimental results roughly with a proper parameter of permeability of buffer surrounding material.
Xia, X.; Kamei, Gento; Iijima, Kazuki; Shibata, Masahiro
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.932, p.933 - 941, 2005/09
To match the demand of establishment of reliable safety assessment methodology for HLW disposalin Japan, sorption behavior of radionuclides is required to be studied for sedimentary rock. Sorption of Se was conducted by batch sorption tests by using sedimentary rock samples and corresponding saline groundwater from Horonobe URL site under reducing condition, with consideration of site-specific conditions. Spectroscopic analyses were performed by X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) after the sorption tests to identify the oxidation states of Se on the sedimentary rock. The sorption tests performed under various parameters allowed to identify that the dominant factors affecting the Se sorption are iron-bearing minerals or oxides and the oganic matter. The XANES analytical results revealed that most Se was Se(0) in the case of natural groundwater, while only some proportions of Se was Se(0) in the case of synthetic groundwater. These suggested that the organic matter probably affect the sorption through changing Se oxidation states, and in a natural sedimentary /saline groundwater system, reduction of selenium to be Se(0), could be expected to be an important sorption mechanism.
Tobitsuka, Sachiko; Iijima, Kazuki; Kohara, Yukitoshi*
Proceedings of 29th International Symposium of Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management (MRS 2005), 0 Pages, 2005/09
The influence of humic acid for the solubility of tetravalent neptunium was investigated under reducing condition, by comparing at various pH. All of experiments were carried in an argon glove-box except analyses. At pH5, 8 and 9, at 20-24 degree C, Np solution in 1E-5 or 1E-3 mol/l was mixed with 0, 5-1,000 mg/l of purified Aldrich humic acid (PAHA). The ionic strength was 0.25 which was brought by 0.1 mol/l NaClO and 0.05 mol/l Na
and 0.05 mol/l Na S
S O
O added as a reductant to keep Np in tetravalent. The concentration of Np was quantified periodically by alpha spectrometry or ICP-MS. With the acid-base titration, analyzed by NICA-Donnan model which assumes the carboxyl group and the phenolic ydroxyl group as two main functional groups, the charge density of PAHA was 2.84, 4.36, 4.78 meq/g at pH5, 8, 9, respectively. In all cases, the total Np concentration ([Np]t) increases with increasing PAHA concentration. In the case of 1E-5 mol/l of initial Np concentration ([Np]
added as a reductant to keep Np in tetravalent. The concentration of Np was quantified periodically by alpha spectrometry or ICP-MS. With the acid-base titration, analyzed by NICA-Donnan model which assumes the carboxyl group and the phenolic ydroxyl group as two main functional groups, the charge density of PAHA was 2.84, 4.36, 4.78 meq/g at pH5, 8, 9, respectively. In all cases, the total Np concentration ([Np]t) increases with increasing PAHA concentration. In the case of 1E-5 mol/l of initial Np concentration ([Np]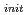 especially, [Np]t increases almost up to [Np]
especially, [Np]t increases almost up to [Np]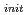 in 50 mg/l PAHA at pH8, 9, or 25 mg/l at pH5. Even in the case of PAHA 5 mg/l, [Np]t becomes one order or more higher than that in the absence of PAHA. The apparent stability constant
in 50 mg/l PAHA at pH8, 9, or 25 mg/l at pH5. Even in the case of PAHA 5 mg/l, [Np]t becomes one order or more higher than that in the absence of PAHA. The apparent stability constant